 The fifth pillar of the CQE Body of Knowledge is Continuous Improvement and it contains 5 main chapters within it:
The fifth pillar of the CQE Body of Knowledge is Continuous Improvement and it contains 5 main chapters within it:
- The 7 Quality Control Tools
- The 7 Quality Management & Planning Tools
- Continuous Improvement Techniques
- Lean Tools
- CAPA (Corrective and Preventative Action)
Continuous Improvement is the second biggest part of the CQE Exam – 27 out 160 questions (17%).
For each of 5 chapters above, you’ll find a quick summary below along with a link to the full chapter.
Each of these chapters contains a practice quiz at the top and bottom of the page.
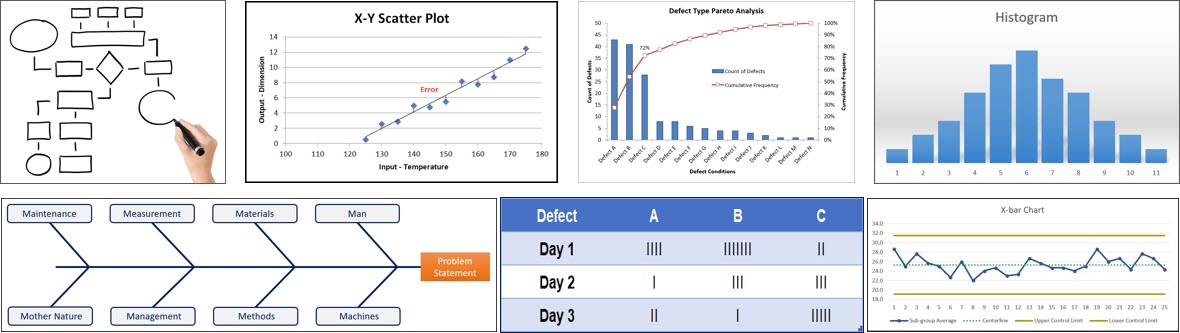
The 7 Quality Control Tools
“A man and his tools make a man and his trade” – Vita Sackville-West
As a Quality Engineer one of the most important skills you can have, is the ability to solve a problem or improve a process.
To do this successfully, you need the proper tools.
In fact, there are 7 specific tool that you must know.
Kaoru Ishikawa once said “As much as 95% of quality problems can be solved with seven fundamental quantitative tools”.
These tools were first categorized as Quality Control Tools by Ishikawa in his book Introduction to Quality Control.
Does it seem odd that we’re in the Continuous Improvement section talking about Quality Control & Problem Solving?
It Shouldn’t. Problem solving is continuous improvement. Improvements happen when we solve problems.
So, what are these 7 fundamental tools for problem solving & continuous improvement:
- Flow Charts
- Check Sheets
- Pareto Charts
- Cause & Effect Diagrams
- Control Charts
- Scatter Diagrams
- Histograms
Within this chapter, we will discuss when to use each tool along with how to construct and analyze them.
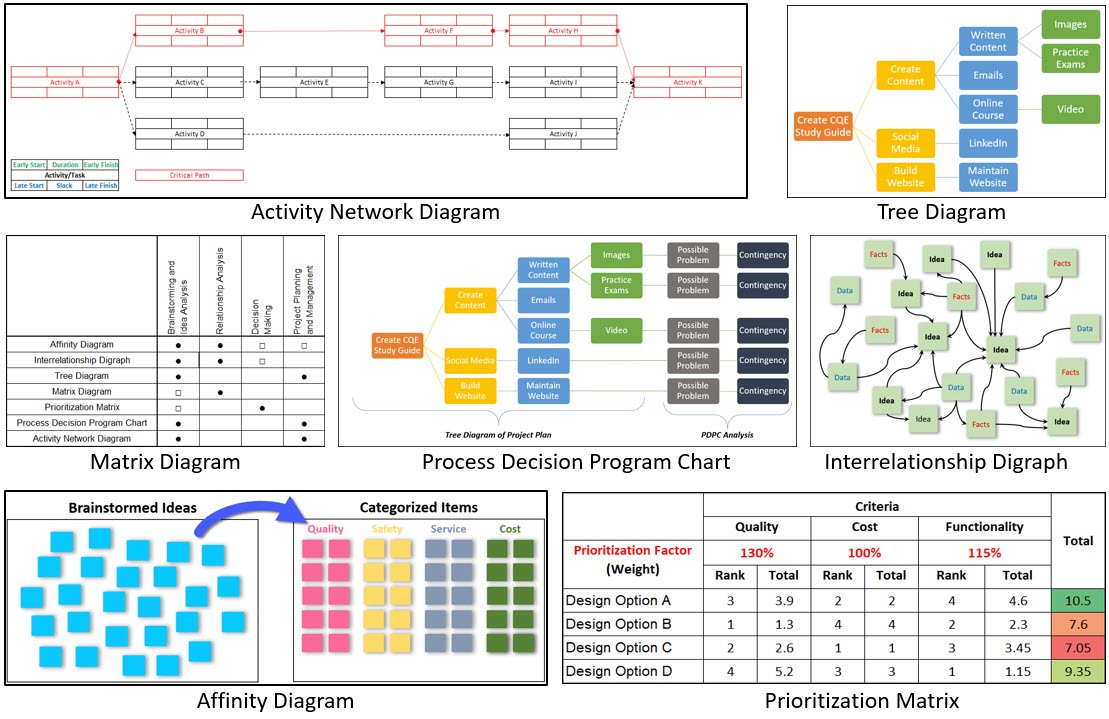
The 7 Quality Management & Planning Tools
The original 7 Quality Control Tools were developed as tools for root cause analysis.
However, improving a process also goes far beyond root cause analysis, you must be resolving issues by making changes to your product or process.
Over time, 7 new tools were developed that were geared more towards the resolution of complex problems– as opposed to simple problem solving.
Complex problems need effective tools to solve them, which is where these 7 new tools shine.
These tools are known as the 7 Quality Management & Planning Tools.
More specifically, these new tools aid us in our ability to brainstorming complex ideas, making tough decision and planning/managing projects.
- Affinity Diagram
- Interrelationship Digraphs
- Tree Diagram
- Matrix Diagram
- Prioritization Matrix
- Process Decision Program Char
- Activity Network Diagram
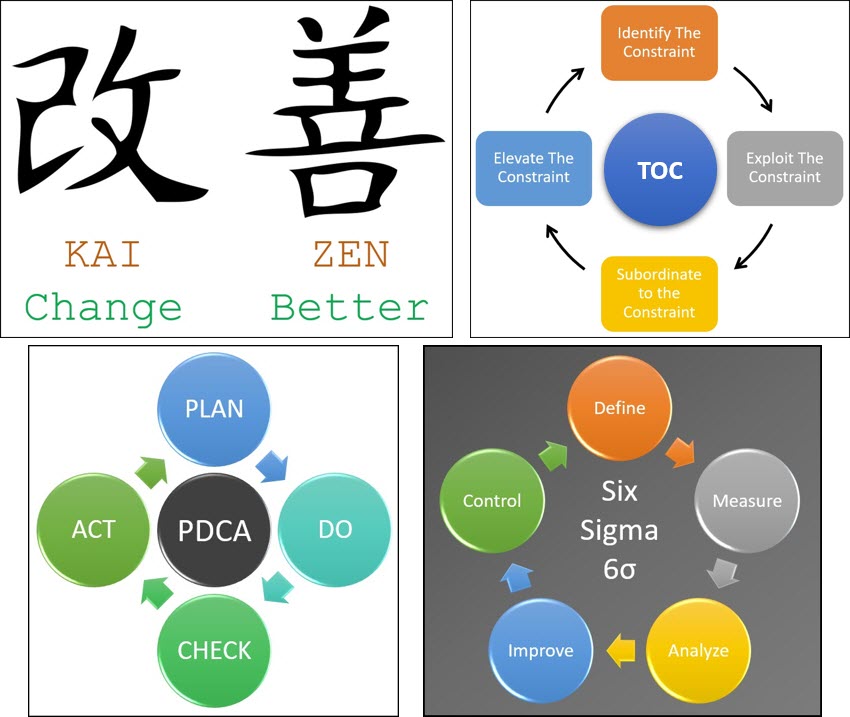
Continuous Improvement Techniques
Continuous Improvement is defined as the on-going efforts within an organization to improve the quality and value of its products, processes or services.
Continuous improvement increases the quality and value of a product.
Continuous Improvement makes an organization more competitive & ensures that an organization keeps up with the changing needs and expectations of the customer.
To truly be successful with a continuous improvement program an organization must be intentional about using a process to achieve improvements and sustain them over time.
The best organization are intentional about using a process to make improvements and sustain them over time.
Over the years, different methodologies have been created to drive continuous improvement.
Within this chapter you will learn how to define and distinguish between these different continuous improvement methodologies:
- Total Quality Management
- Kaizen
- Plan-Do-Check-Act (PDCA)
- Six Sigma
Lean Tools
Lean Manufacturing is a unique perspective on successful manufacturing that has had a huge impact on the 20th and 21st century.
Part 1 of this chapter is a review of the History of Lean, and the 5 Principles of the Lean Production System.
What you’ll learn is that lean practitioners are focused on creating more value for your customers with fewer resources.

Many of the core tools within Lean are used to improve the value creating processes to provide value while removing non-value adding activities (waste).
Part 2 of this chapter includes a review of the 8 Major Lean Tools used within the lean management system:
- The 8 Deadly Wastes (Muda)
- 5S
- The Value Stream Map
- Kanban
- Visual Control
- Standard Work
- Takt Time
- Single Minute Exchange of Die (SMED)
- Overall Equipment Effectiveness
We then wrap up the chapter quickly in Part 3, which is a glossary of other lean topics, tools and techniques that you might run across.
CAPA – Corrective & Preventative Action
Corrective and Preventative Action or CAPA is the last and final chapter of the Continuous Improvement section.
These two concepts, Corrective action and preventative action are similar and different.
These activities are similar in that they are meant to address a quality problem, often called a non-conformance.
A non-conformance is described as any issue where your product does not conform to a specification or requirement. This could be a customer requirement, a regulatory requirement, a safety requirement, etc.
These activities are different in that a corrective action is meant to address an issue that has already occurred, and a preventative action addresses potential issues that have not yet occurred.
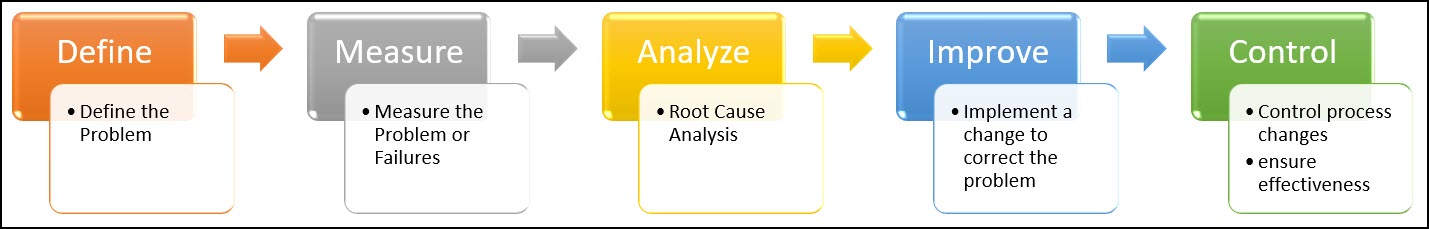
This chapter will cover both Corrective Action and Preventative Action, and will outline the process and key tools used within both arenas.
A corrective action is any action taken to address a quality issue. The CQE Body of Knowledge outlines the 6 steps process for corrective action:
- Problem Identification,
- Failure Analysis,
- Root Cause Analysis,
- Problem Correction,
- Recurrence Control,
- Verification of Effectiveness.
The second portion of the CAPA process is that of Preventative Action.
Preventative action is very common in Quality, in fact the modern-day quality management system has been designed to encourage and promote preventative actions.
Beyond these tools however, this chapter will focus mainly on the following 3 preventative action tools:
- Error proofing/poka-yoke,
- Robust design,
- Analyze their effectiveness
Ready to see the next Major Pillars: Risk Management, The Quality System, Management & Leadership, Product & Process Design, Product & Process Control & Statistics.
Have a comment question or concern? Please don’t hesitate to Contact Me.
