Your Quality System, is a combination of all the activities that your organization uses to direct, control, and coordinate quality.
Your Quality System, is a combination of all the activities that your organization uses to direct, control, and coordinate quality.
To effectively achieve high levels of Quality, you must assure quality at all phases in your product lifecycle.
All the way from the early research and design phases to the final distribution and eventual retirement of the product.
Quality can then be broken down into a few discrete phases include quality planning, quality control, quality assurance, and quality improvement.
This approach will allow you to continually satisfy and exceed your customers needs and expectation (delivery quality).
ISO As a Guide to the Quality System
The International Organization for Standardization, ISO, has gone to great lengths to define a Quality Management System which can be used by organizations of all types & sizes.
The ISO QMS is used by organization who wish to demonstrate that they are capable of consistently delivering a product that meets their customers’ needs and continuously improving their performance.
The ISO Quality Management System takes a process approach to achieve the ongoing control needed to achieve customer satisfaction.
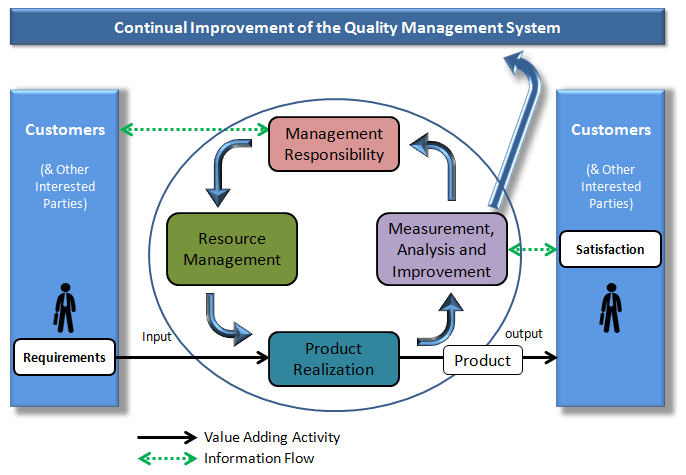
ISO’s Process Model for Quality Management
Everything starts and ends with the customer.
Customers define the product requirements (inputs), and then receive the product (output) and communicate back their level of satisfaction.
The process model also defines two different processes for information flow.
The first is the communication between Top Management & the Customer regarding the organizations intentions for Quality.
The second is the feedback from the customer to the organization regarding the customers current level of satisfaction.
Finally, your Measurement, Analysis and Improvement processes must be based on the customers feedback and must result in an improvement of your Quality Management System.
4 Primary Areas of the Quality System Model
Within the ISO Model, you can see 4 primary areas associated with the Quality System, which are all interrelated to each other:
- Management Responsibility
- Resource Management
- Product Realization
- Measurement, Analysis & Improvement
Within each of these 4 areas you will find the basic elements of the Quality System.
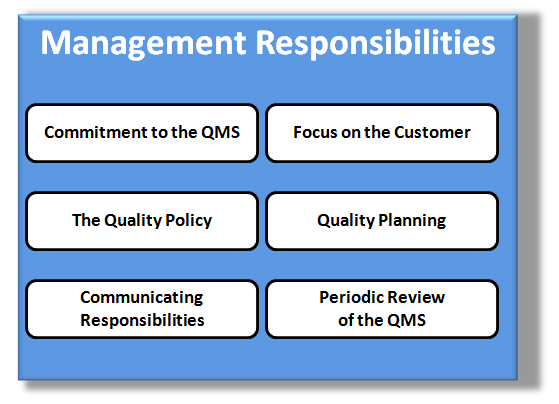
Management Responsibility
ISO defines 6 Management Responsibilities within the Quality System, which include:
- A commitment to develop, implement and maintain a Quality System and continually improve its effectiveness
- Maintaining a focus on the customer as to ensure all customer needs are met
- Authoring & communicating a Quality Policy that documents their commitment to the customer
- Planning Quality Objectives & cascading those down to the functional areas for implementation
- Define & Communicate the Responsibilities & Authorities within the organization including the Management Representative
- Periodically Reviewing the organizations Quality System (Auditing) to ensure continued effectiveness and look for opportunities for improvement
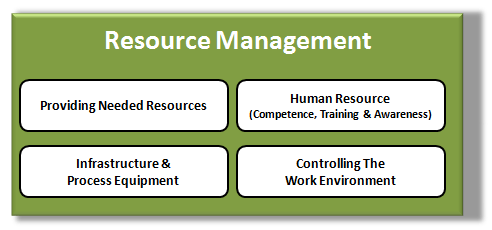
Resource Management
This area of your Quality System includes the following basic elements which all can impact your final quality level. Your Organization should therefore control & ensure:
- Adequate levels of resources have been provided to maintain and improve the organizations Quality Management System
- That the Human Resources affecting conformity to product requirements are competent, trained & aware of the importance of their activities
- That the Infrastructure (buildings, workspaces, Utilities) & Process Equipment are maintained in order to support product conformity (Quality)
- That they are managing the Work Environment needed to achieve product conformity (Quality)
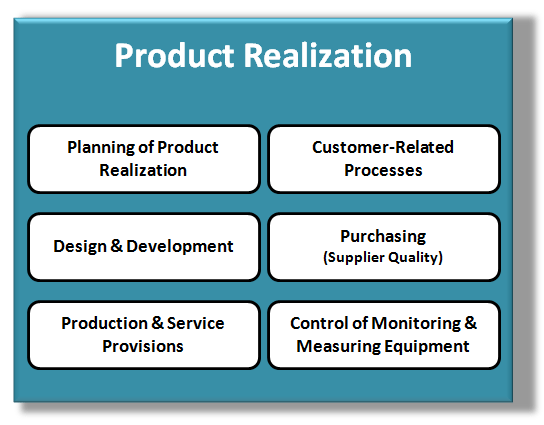
Product Realization
Product Realization is the collection of interrelated processes that are used to design, manufacture & control your product. This area includes ~50% of the Quality System elements and spans the following 6, very broad topics:
- The early planning process associated with the Product Realization process
- Defining the Customer-Related Processes needed to determine your customers needs & requirements
- The entire Design & Development process including Design Inputs, Outputs, Reviews, Verification & Validation
- The Purchasing Controls needed to qualify and maintain suppliers and ensure conformance of supplied product
- The Production & Service Provisions associated with controlling processes, product verification & final distribution
- The Control of Monitoring & Measuring Equipment required to ensure product conformance during testing
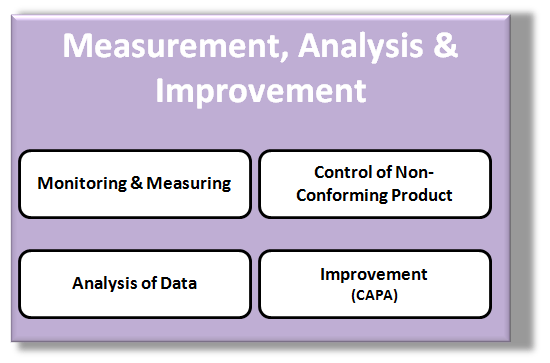
Measurement, Analysis & Improvement
The final area of your Quality System include the 4 basic elements associated with Measurement, Analysis & Improvement:
- Monitoring & Measuring data related to customers perception of the organizations ability to meet their needs
- Controlling Non-Conforming Product to prevent its unintended use or delivery
- Analysis of Data to demonstrate the effectiveness & suitability of the Quality System
- Continual Improvements to the Quality System via the CAPA System
Conclusion
Your Quality System is the collection of the interrelated processes and activities that are meant to ensure that your product or service meets the needs & requirements of the customer.
ISO provides a solid framework for the Quality System which many of the basic elements of a Quality System, shown below: